Introduction to Gift Deed
Ever thought of gifting property to someone special? That’s where a it comes into play. It’s a legal way to transfer property ownership without any exchange of money. Whether you’re gifting your child a flat or donating land to a temple, it ensures the transfer is valid, lawful, and binding.What Is a Gift Deed?
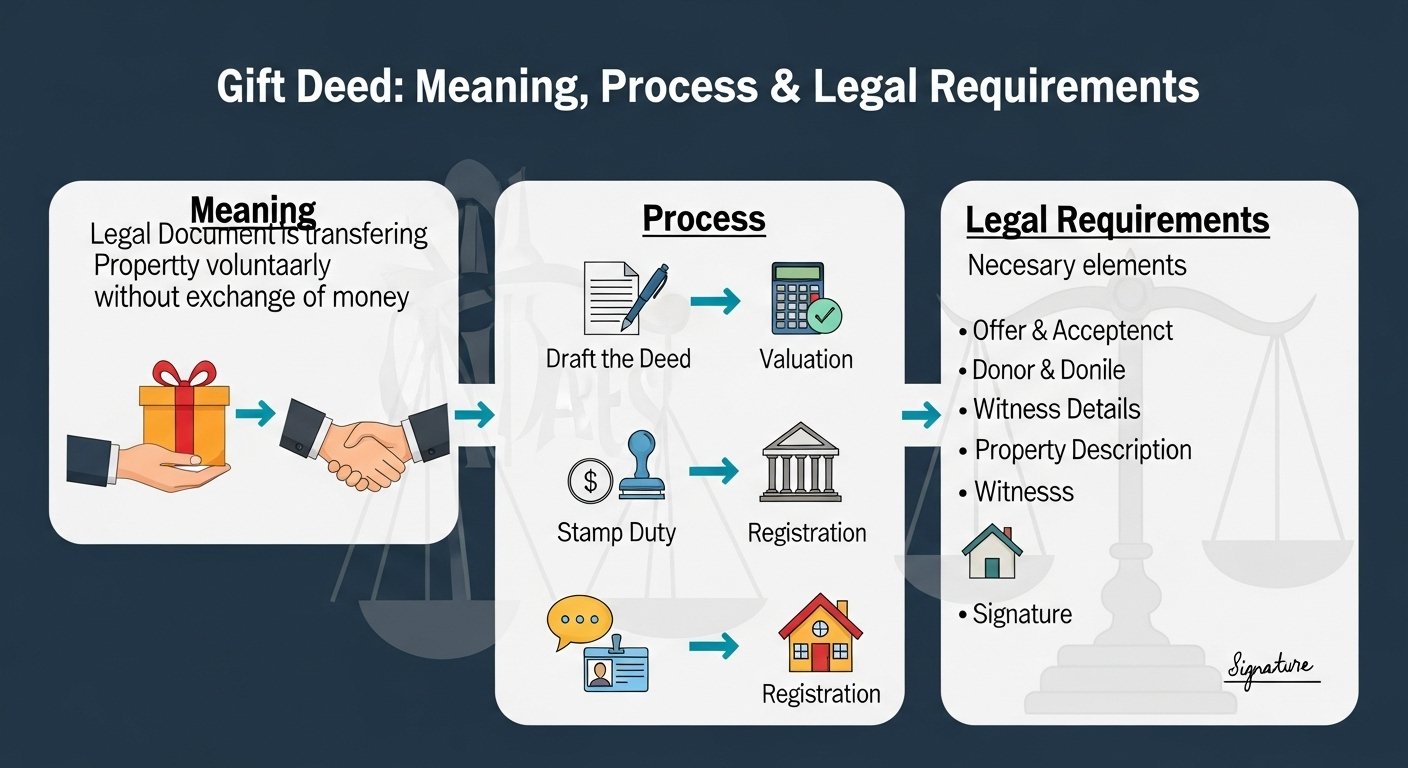
it is a legal document used to transfer ownership of movable or immovable property from one person (the donor) to another (the donee) voluntarily, without any monetary exchange.
Under Section 122 of the Transfer of Property Act, 1882, such a transfer is recognized only when it is made voluntarily and accepted by the donee during the donor’s lifetime.
Importance of a Gift Deed
It is not just a gesture—it’s a legal safeguard. It ensures that your gift can’t be disputed later and provides a record of ownership transfer. Some reasons why it’s essential include:
Provides legal proof of transfer
Prevents future property disputes
Helps avoid inheritance complexities
Useful for tax documentation and record-keeping
Legal Framework Governing Gift Deeds in India
It IS governed by the Transfer of Property Act, 1882 and the Registration Act, 1908. For a gift to be legally valid:
The deed must be registered.
It must be made voluntarily and accepted by the donee.
The property must exist at the time of gifting.
Parties Involved in a Gift Deed
Donor (The Giver)
The donor is the person who owns the property and decides to gift it to another individual or entity. The donor must be competent to contract, meaning they must be of sound mind and an adult.
Donee (The Receiver)
The donee is the individual or organization receiving the gift. They must accept the gift during the donor’s lifetime for the transfer to be valid.
Essential Elements of a Valid Gift Deed
Voluntary Transfer
The transfer must be made out of free will—without coercion, fraud, or undue influence.
Ownership of Property
The donor must have complete ownership of the property being gifted.
Acceptance by the Donee
The donee must accept the gift either in writing or by taking possession of the property. Without acceptance, the gift has no legal effect.
Types of Properties That Can Be Gifted
Movable Property
Includes items like jewelry, vehicles, or cash that can be physically moved from one place to another.
Immovable Property
Covers assets like land, houses, or apartments that are fixed and cannot be physically moved.
How to Draft
A Gift Deed should be drafted carefully to ensure clarity and avoid disputes later.
Key Clauses to Include
Details of the donor and donee
Complete property description
Voluntary declaration of the gift
Donee’s acceptance clause
Rights and liabilities (if any)
Signature of witnesses
Language and Legal Format
Use clear, simple language. The deed should be executed on non-judicial stamp paper of value prescribed by the respective state.
Step-by-Step Process of Gift Deed Registration
1. Drafting the Deed
The deed should be prepared by a qualified legal professional to ensure accuracy and compliance with local laws.
2. Paying Stamp Duty
Before registration, stamp duty must be paid based on the property’s market value and local government rules.
3. Registering at the Sub-Registrar’s Office
Both parties must be physically present (or represented through Power of Attorney) at the Sub-Registrar’s office. The officer verifies documents, identities, and witnesses before finalizing registration.
Documents Required for Registration
Original Gift Deed
ID proofs (PAN, Aadhaar, Passport)
Property documents (previous title deed, tax receipts)
Passport-sized photographs
Encumbrance certificate
Proof of stamp duty payment
Stamp Duty and Registration Charges
Stamp duty varies from state to state. For example:
Gifts to family members often attract lower duty rates (e.g., 1% or nominal charges).
Gifts to non-relatives may incur standard stamp duty (usually 4–6%).
Registration fees are typically around 1% of the property value.
Tax Implications of a Gift Deed
Gifts from Relatives
Gifts received from specified relatives (like parents, siblings, or spouse) are exempt from income tax, regardless of value.
Gifts from Non-Relatives
If the gift value exceeds ₹50,000, it becomes taxable under the head ‘Income from Other Sources’ as per the Income Tax Act, 1961.
Revocation or Cancellation
A Gift Deed can only be canceled under specific conditions, such as:
Mutual consent between donor and donee.
Proven fraud, misrepresentation, or coercion.
If the donee fails to meet a condition mentioned in the deed.
Once registered, unilateral cancellation isn’t allowed without a court order.
Difference Between Gift Deed and Will
| Aspect | Gift Deed | Will |
|---|---|---|
| When Effective | During the donor’s lifetime | After the testator’s death |
| Registration | Mandatory | Optional |
| Revocation | Difficult once registered | Can be changed anytime |
| Ownership Transfer | Immediate | Post-death |
Advantages of Executing
Immediate transfer of ownership
Legally binding and secure
Saves time compared to inheritance procedures
Reduces chances of future disputes
Tax benefits for gifts to relatives
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Failing to register the Gift Deed
Missing signatures or witness details
Using vague property descriptions
Ignoring tax and stamp duty rules
Conclusion
It is one of the most efficient ways to transfer property ownership within your family or to a loved one. It brings transparency, legality, and peace of mind to both parties involved. But remember—always register the deed and seek legal guidance to ensure a smooth, dispute-free transaction.
FAQs
1. What is a Gift Deed?
A Gift Deed is a legal document that transfers property ownership from one person to another without any monetary consideration.
2. Is registration of a Gift Deed mandatory?
Yes, as per the Registration Act, 1908, it must be registered to be legally valid.
3. Can a Gift Deed be revoked?
Yes, but only under mutual consent or by a court order in cases of fraud or coercion.
4. Do I have to pay tax on gifted property?
Gifts from relatives are tax-free, while those from non-relatives exceeding ₹50,000 are taxable.
5. What’s the benefit of a Gift Deed over a Will?
A Gift Deed transfers ownership immediately, while a Will takes effect only after death.